Research Articles
Synchrotron Radiation in Protein Crystallography: Accelerating Structural Biology and Drug Discovery
This article explores the transformative role of synchrotron facilities in protein crystallography, a cornerstone technique in modern structural biology.
Protein Data Bank Decoded: A Researcher's Guide to Structures, Analysis, and Drug Discovery
This guide provides researchers, scientists, and drug development professionals with a comprehensive framework for navigating and utilizing the Protein Data Bank (PDB).
Beyond the Coordinates: A Practical Guide to Interpreting, Validating, and Applying PDB Crystallography Data
This guide provides researchers, scientists, and drug development professionals with a comprehensive framework for interpreting Protein Data Bank (PDB) files from crystallography.
Protein Crystallization for Beginners: A 2025 Guide from Principles to Practice
This guide provides a comprehensive introduction to the protein crystallization process, a critical step in X-ray crystallography for determining 3D protein structures.
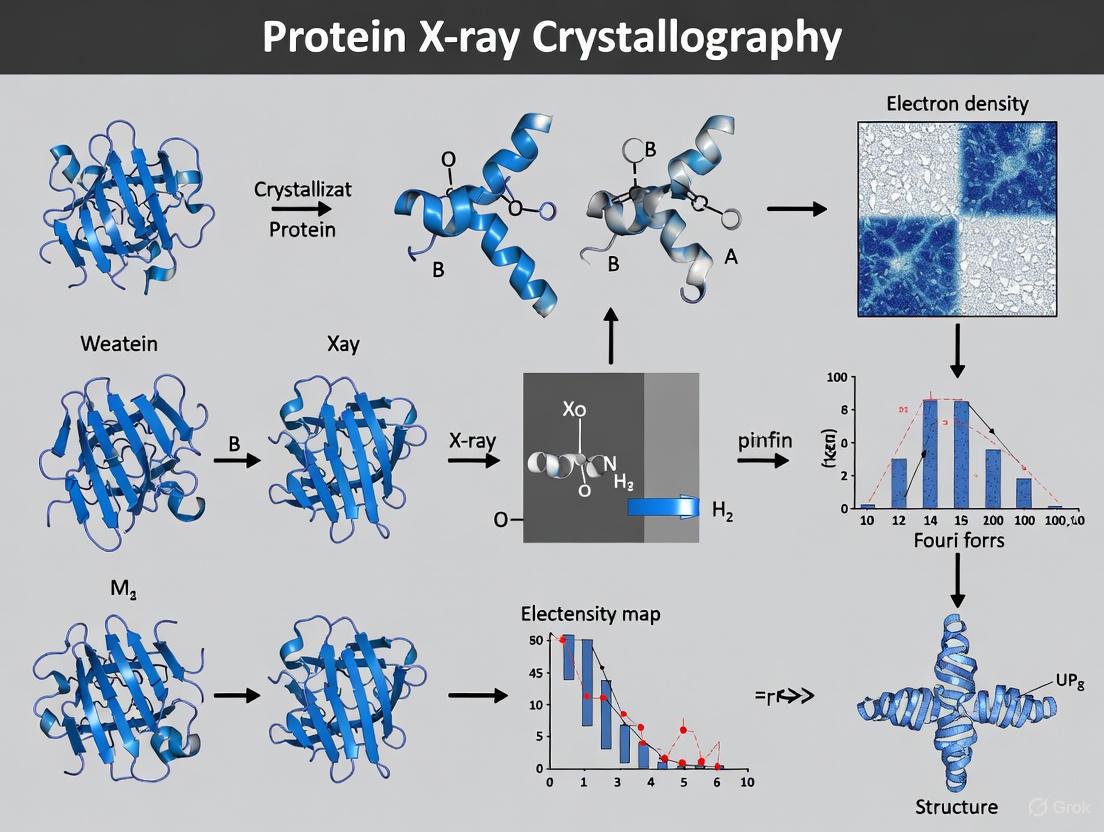
Protein X-Ray Crystallography: Principles, Methods, and Applications in Drug Discovery
This article provides a comprehensive guide to protein X-ray crystallography, tailored for researchers, scientists, and drug development professionals.
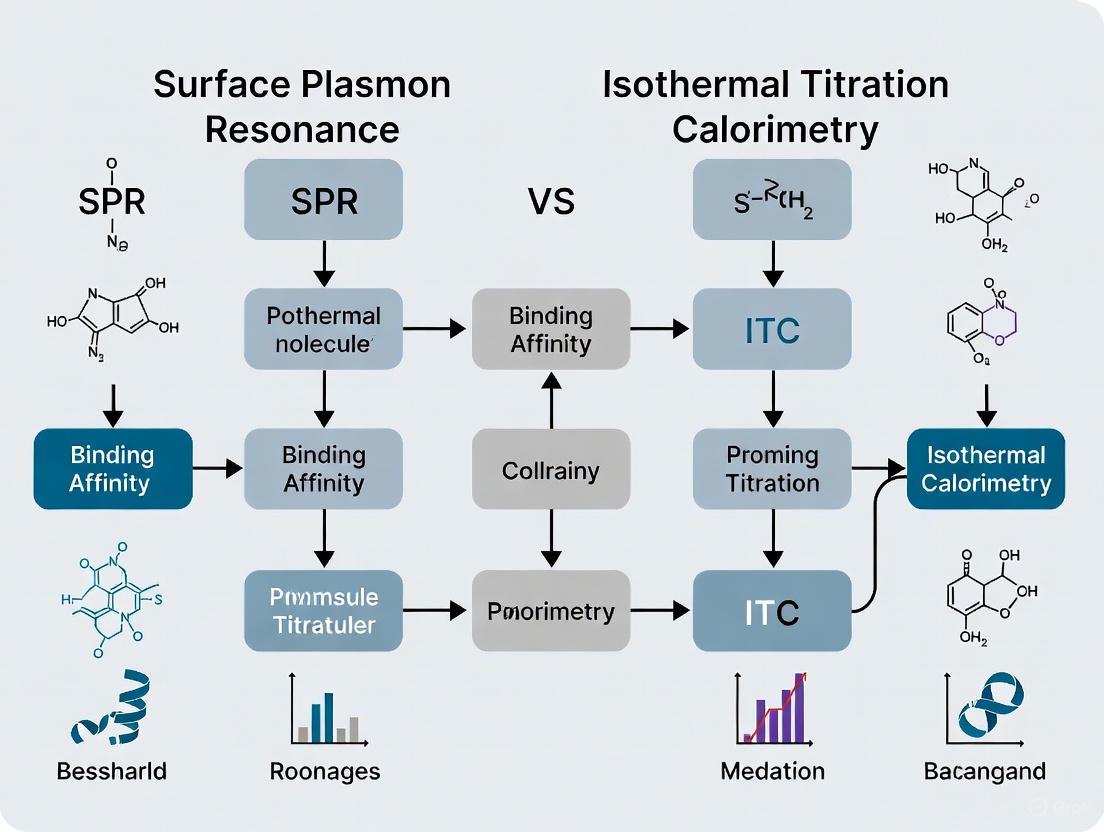
SPR vs ITC: Choosing the Right Method for Protein-Small Molecule Binding Analysis
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) and Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) for characterizing protein-small molecule interactions, a critical task in drug discovery and biophysical research.
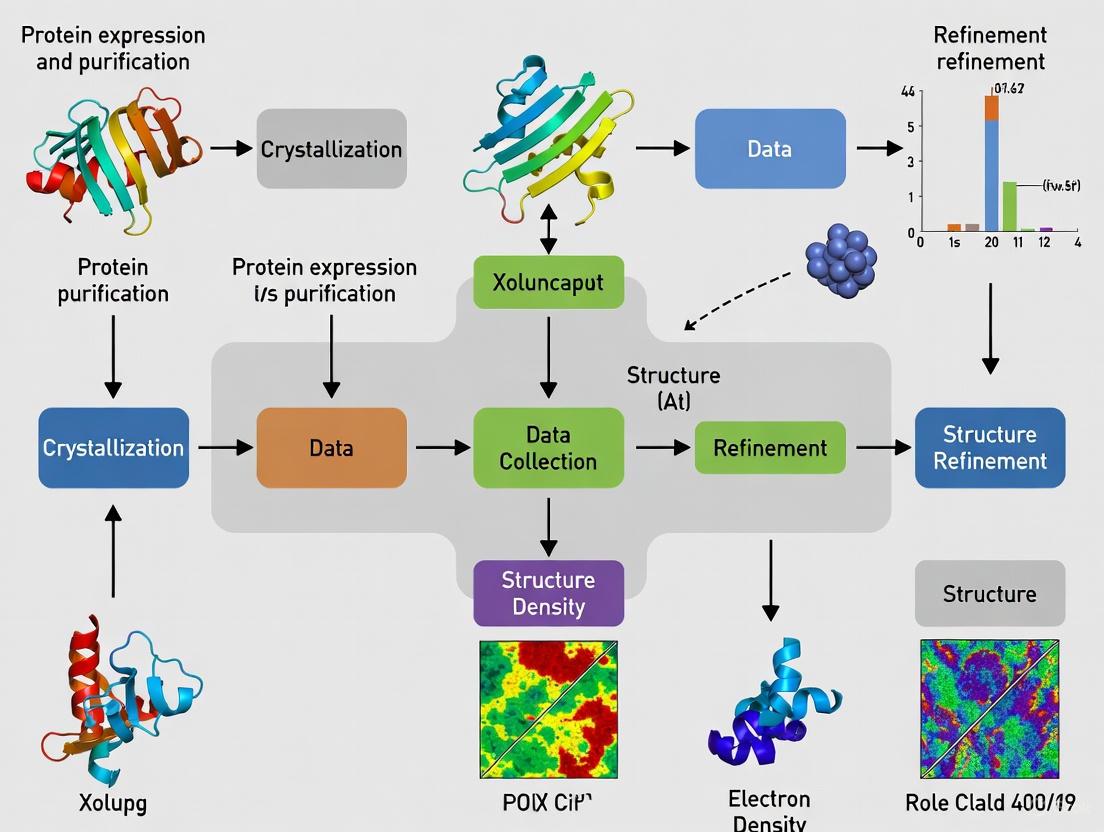
Protein Structure Determination by X-Ray Crystallography: A Comprehensive Guide from Principles to Practice
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the protein structure determination pipeline using X-ray crystallography, a cornerstone technique in structural biology.
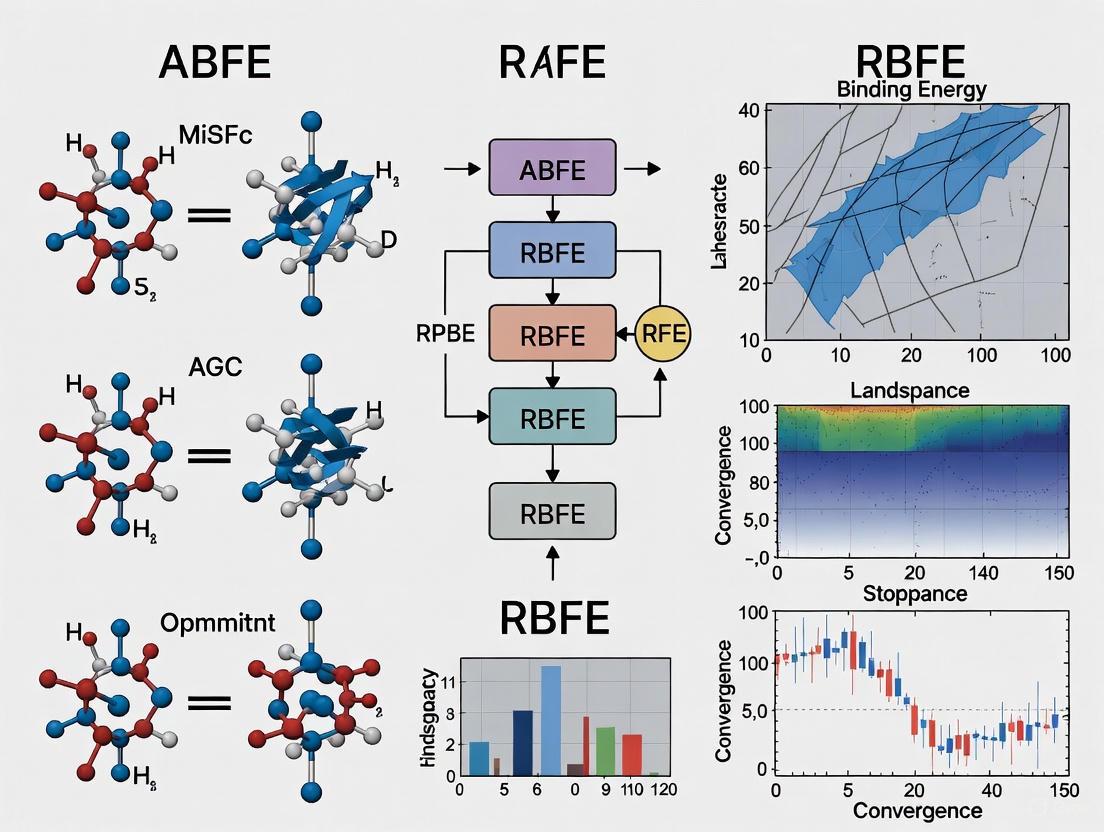
ABFE vs RBFE: A Strategic Guide to Binding Free Energy Methods in Drug Discovery
Accurate calculation of protein-ligand binding affinity is a cornerstone of modern computational drug discovery.
Validating LABind: A New Era of Ligand-Aware Binding Site Prediction for Unseen Ligands in Drug Discovery
Accurately predicting protein-ligand binding sites is crucial for drug discovery, but a significant challenge lies in generalizing predictions to novel, unseen ligands.
Validating Hot-Spot Residues by Alanine Scanning: A Guide for Drug Discovery Scientists
This article provides a comprehensive resource for researchers and drug development professionals on the validation of hot-spot residues through alanine scanning mutagenesis.